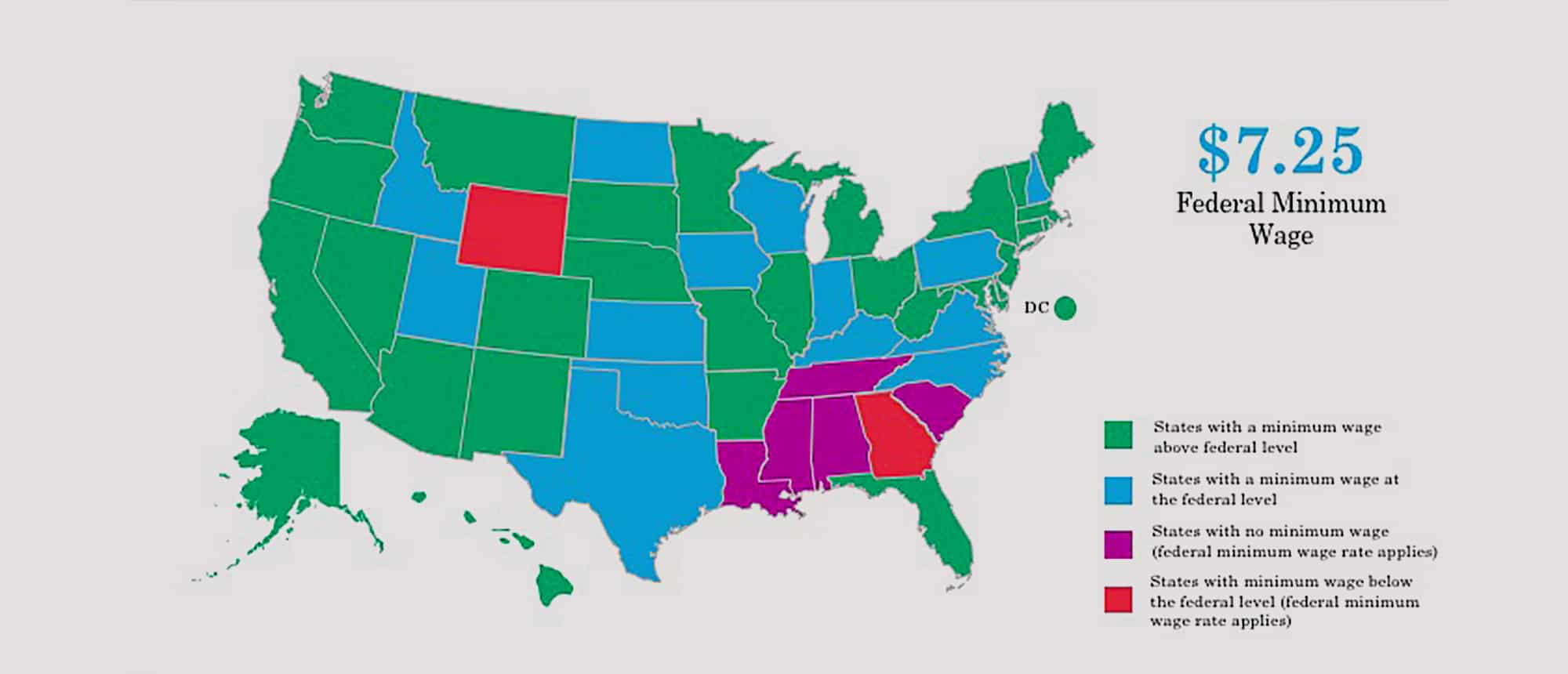
State Minimum Wage Laws
While the Federal minimum wage is $7.25, different state governments have different laws regulating the minimum wage within that state. The map below from the Department of Labor shows which states have minimum wage laws above the federal level, at the federal level, no minimum wage laws, or minimum wage laws below the federal level.
The state minimum wage rate requirements, or lack thereof, are generally controlled by legislative activities within the individual states.
Federal minimum wage law supersedes state minimum wage laws where the federal minimum wage is greater than the state minimum wage. In those states where the state minimum wage is greater than the federal minimum wage, the state minimum wage prevails.
There are 2 states than have a minimum wage set lower than the federal minimum wage. There are 29 states plus the District of Columbia with minimum wage rates set higher than the federal minimum wage. There are 14 states that have a minimum wage requirement that is the same as the federal minimum wage requirement. The remaining 5 states do not have an established minimum wage requirement.
The District of Columbia has the highest minimum wage at $11.50/hour. The states of Georgia and Wyoming have the lowest minimum wage ($5.15/hour) of the 45 states that have a minimum wage requirement.
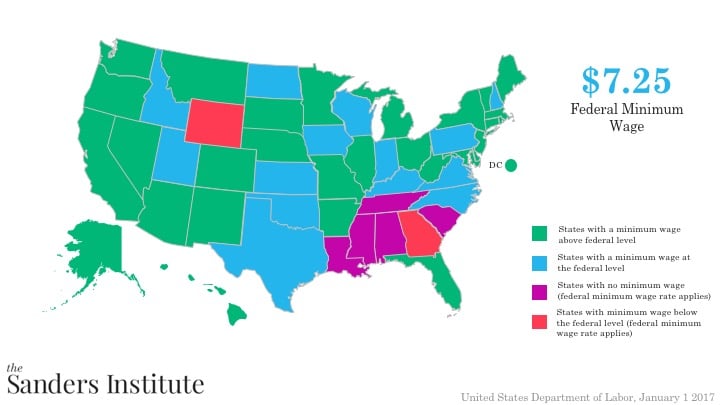
Note: There are 12 states (AK, AZ, CO, FL, MO, MT, NJ, NV, OH, OR, SD, and WA) that have minimum wages that are linked to a consumer price index. As a result of this linkage, the minimum wages in these states are normally increased each year, generally around January 1st. The exception is Nevada which adjusts in the month of July each year. Effective January 1, 2017, seven (7) of the 12 states increased their respective minimum wages.