The following is a summary of the Congressional Research Service on the minimum wage.
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) of 1938 established the hourly minimum wage rate at 25 cents for covered workers. Since then, it has been raised 22 separate times, in part to keep up with rising prices. Most recently, in July 2009, it was increased to $7.25 an hour. Because there have been some extended periods between these adjustments while inflation generally has increased, the real value (purchasing power) of the minimum wage has decreased substantially over time.
The minimum wage is not indexed to the price level. It has been legislatively increased from time to time to make up for the loss in its real value caused by inflation. In nominal (current dollar) terms, the minimum wage has risen steadily from 25 cents to $7.25 an hour, where it has remained since its effective date of July 2009. As the legislated adjustments to the minimum wage standard have occurred at irregular intervals—sometimes increasing annually, other times not for several years—while prices have generally risen each year, the purchasing power (real or constant dollar value) of the minimum wage has varied considerably since its enactment.
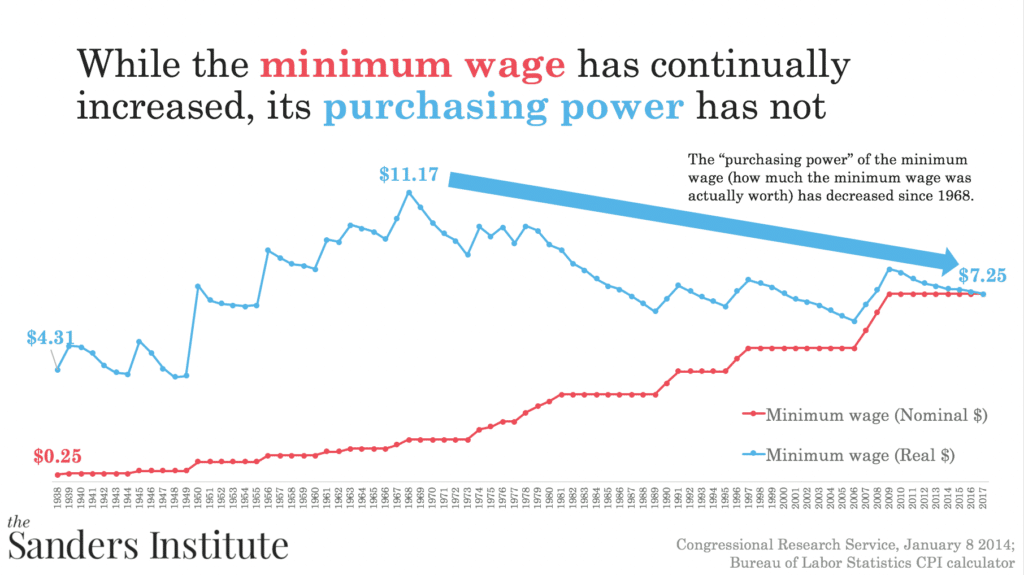
For each time the minimum wage was changed, the graph above presents its nominal and real value. The inflation adjustments to the minimum wage are made using the Consumer Price Index for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers (CPI-W). Real values of the minimum wage are expressed in terms of July 2017 dollars, the latest month for which the index is available at the time of this Sanders Institute article’s preparation.
The peak value of the minimum wage in real terms was reached in 1968. Although the nominal value of the minimum wage was increased between 1968 and 2009, these legislated adjustments did not enable the minimum wage to keep pace with the increase in consumer prices, so the real minimum wage fell.